Carry trade – the earning strategy on cross-rates. Anton Hanzenko.
The article “Cross Rates Trading. Features ” was published earlier in the trader’s blog, which dealt with the peculiarities of trading on cross-rates and about some of their subtleties. Today we will dwell on the concept of Carry trade.
Carry trade is a trading strategy based on the different yields of various interest rates that the central bank (CB) determines. Each world currency has its own key rate, which is set by the Central Bank and the higher this rate is relative to others, the more attractive this currency is.
Features of the Carry trade strategy
For trading in the Forex market, the Carry trade strategy is excellent for cross-rates, especially for those with the Japanese yen (JPY). The Japanese yen is a unique currency due to its stability and monetary policy of the Bank of Japan, which is aimed at negative profitability. Also, a very convenient currency is the Swiss franc (CHF).
Unlike majors (pairs containing an American dollar), cross rates are more suitable for the Carry trade due to its variability and specifics. Often the strategy does not work so clearly on pairs with the US dollar due to its high political dependence.
The main criterion of Carry trade is the key rate. Currencies with a high interest rate are always more preferable to currencies with a low interest rate.
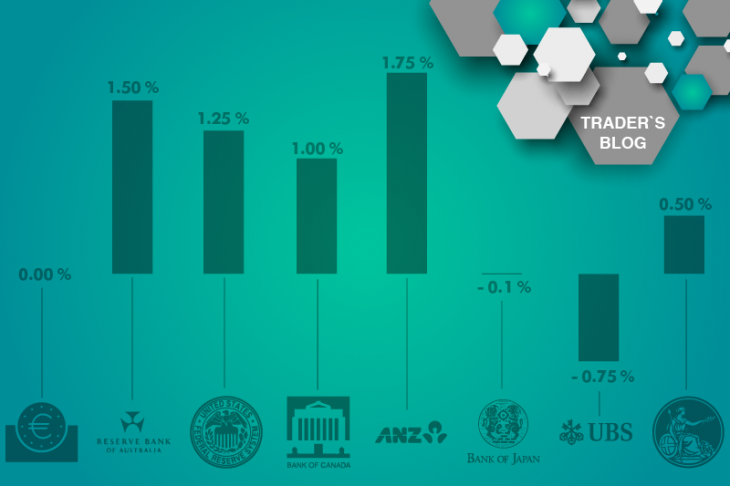
Interest rates of major world banks:
The United States (Federal Reserve System) – 1.00 – 1.25%
EU (European Central Bank) – 0.00%
Switzerland (Swiss National Bank) – -0.75%
Australia (Reserve Bank of Australia) – 1.50%
United Kingdom (Bank of England) – 0.50%
Japan (Bank of Japan) – -0.1%
Canada (Bank of Canada) – 1.00%
New Zealand (Reserve Bank of New Zealand) – 1.75%
Also, in addition to the actual interest rates, it is necessary to monitor the possibility of their change and data affecting it. These are data on: employment, inflation, GDP, forecasts for economic development and plans for the economy of a country. Expectations of changes in rates and news that may affect interest rates in Carry trade act out the main role.
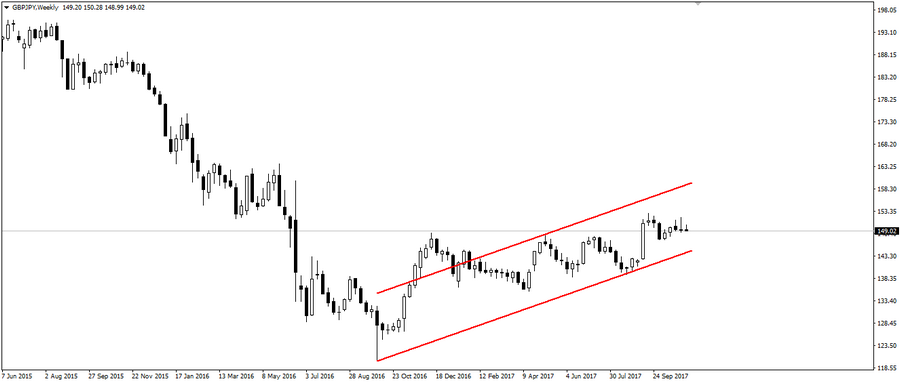
One of these instruments is the pair GBP/JPY, which was caused by the change in the direction of the monetary policy of the Bank of England due to the withdrawal of the UK from the EU.
As a result, a change in the overall global trend for this pair can be traced.
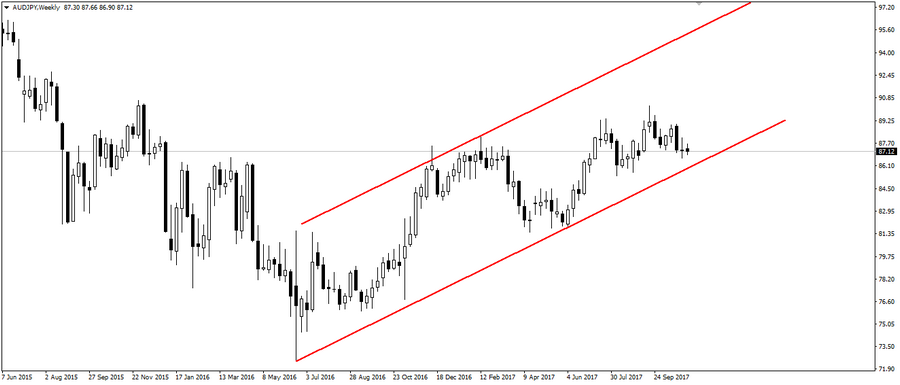
The second example is the pair AUD/JPY, which demonstrates an even steeper uptrend, which is also caused by the difference in interest rates and monetary policies.
The Carry trade strategy is a very effective strategy with medium and long-term investments. But, like all medium and long-term investments, Carry trade has the same drawbacks. Also, this strategy can serve as a filtering strategy, which will significantly increase the percentage of profitable trades.
Anton Hanzenko