
Risks of global economic slowdown are escalating
.Since October 2019, pessimistic sentiments regarding the prospects of the global economy intensified sharply. A series of statements by the major world politicians and macroeconomic indicators were the reason.
Political factors
The actions of world’s major Central Banks (CBs) became the political signals indicating a slowdown in the global economy. In the second half of 2019, they started key interest rates cuts.
- Thus, the US Federal Reserve twice reduced rates by 25 b. p. to the mark of 2.00%.
- The ECB has left key interest rates unchanged. They also announced the resumption of the quantitative easing program and applied a multi-level rate system.
- The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) has cut rates three times since June this year by 25 b. p. to the mark of 0.75%.
And this is only the part of the actions of the world’s Central Banks aimed at stimulating the national economy. But most importantly, all world’s major banks do not deny the possibility of further stimulating the economy, if necessary.
We can say that Central Banks are proactive and have protected themselves from a slowdown in the global economy by stimulating measures, actually preparing for the worst, but alas, this is not so. Since active stimulus measures began only now, in the second half of 2019, and signs of a recession and a trade war have been traced for more than a year.
IMF Forecasts
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has lowered its expectations for growth in world GDP four times since last October. The IMF cited a number of reasons, among which the trade war between the United States and China came first. Also were noted:
- the uncertainty around Brexit,
- U.S. trade duties on major trading partners
- and geopolitical tensions in the Middle East.
IMF First Deputy Managing Director David Lipton noted an increase in signs of a slowdown in the world economy at a faster pace than previously seen in his speech on October 1, pointing to a strong likelihood of another decrease in IMF forecasts for the global economy. The forecast for world GDP growth for 2019 is 3.2%, 2020 – 3.5%.
Macroeconomic indicators
The GDP growth rates of large countries all show a slowdown.
U.S. GDP growth rate
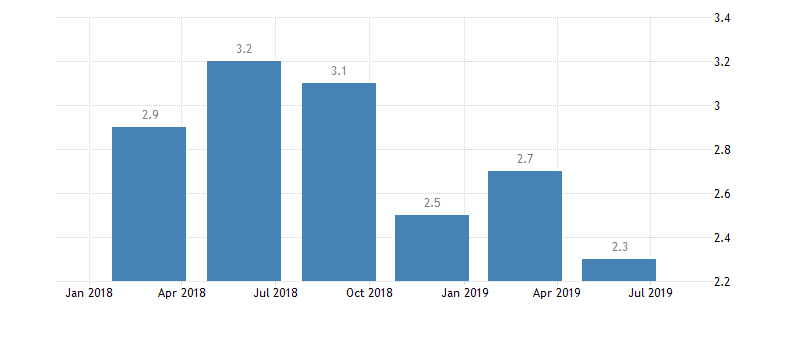
Eurozone GDP growth rate
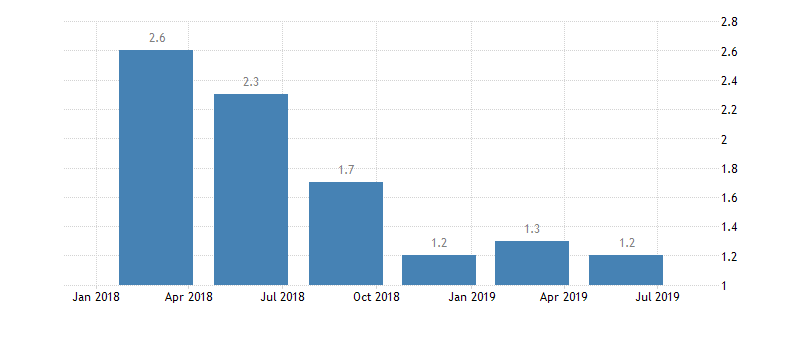
U.K. GDP growth rate
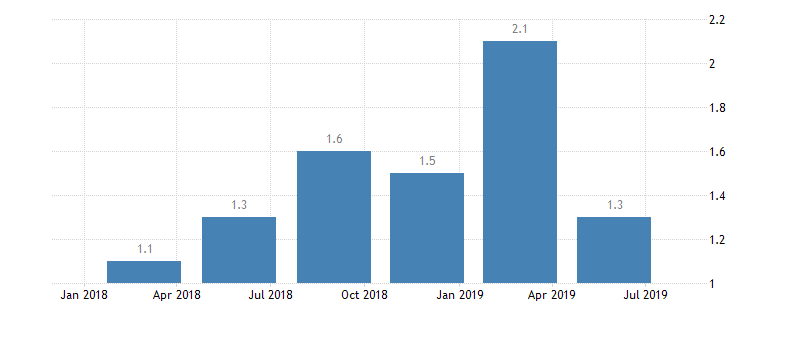
German GDP growth rate
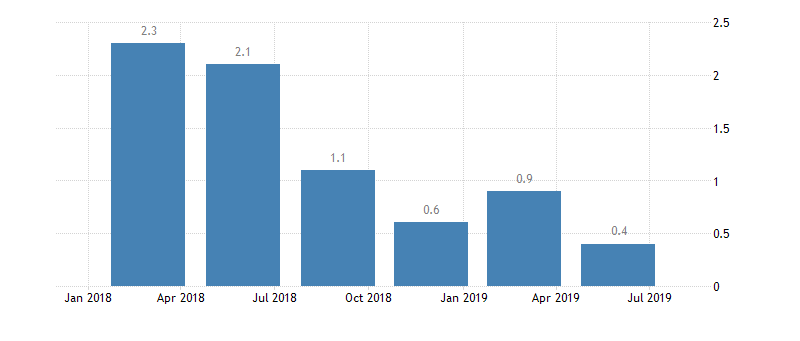
China’s GDP growth rate
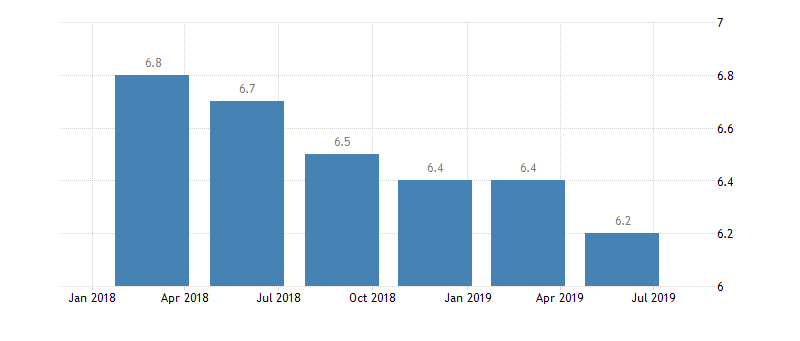
Australia’s GDP growth rate
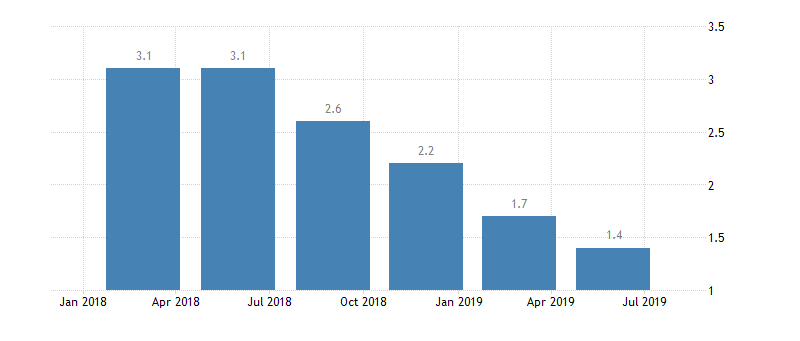
The recession process has just begun to gain momentum. It approached zero levels of the GDP growth rates. The key drivers that caused the global economic slowdown remain relevant. The market expects a significant recession, if not a new crisis.
Anton Hanzenko